ASTM A686 W1 Tool Steel Drill Rod

W1 steel ASTM A686 W1 Tool Steel Drill Rod
1 W1 steel Introduction
w1 steel Water-hardening tool steels are also known as group W steels. This group consists of three types, namely, W1 tool steel, W2 tool steel, and W3 tool steel. The main alloying element found in group W steels is carbon. To increase the wear resistance and hardenability of the W steels, a small amount of chromium can be added. By adding vanadium, the grain size is maintained, which enhances the toughness of the steels. The group W steels have low resistance to softening at high temperatures and are inexpensive.
The W1 tool steel is one of the most commonly available water hardening tool steel grades and can be easily hardened by heating and quenching in water. However, this alloy does undergo some amount of distortion during quenching.
Other designations that are equivalent to AISI W1 tool steels include:
- ASTM A686
- SAE J437 (W108), (W109), (WhO), (W112)
- SAE J438 (W108), (W109), (W110), (W112)
- UNS T72301
2 w1 steel Applications
The W1 tool steel is mainly used for cold heading, hand-operated metal cutting tools, reamers and embossing taps. It is also used for cutlery.

3 Quality Standard
ASTM A686 Standard Specification for Carbon Tool Steel
4 w1 steel Chemical Composition(%)
| Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Mo | V | W | Cu | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade A | 0.70-1.50 | 0.10-0.40 | 0.10-0.40 | 0.030 max | 0.030 max | 0.15 max | 0.10 max | 0.10 max | 0.15 max | 0.20 max | 0.20 max |
| Grade C | 0.70-1.50 | 0.10-0.40 | 0.10-0.40 | 0.030 max | 0.030 max | 0.30 max | 0.10 max | 0.10 max | 0.15 max | 0.20 max | 0.20 max |
Smelting Option
1 EAF: Electric Arc Furnace
2 EAF+LF+VD: Refined-smelting and vacuum degassing
3 EAF+ESR: Electro Slag Remelting
4 EAF+PESR: protective atmosphere Electro Slag Remelting
5 VIM+PESR: Vacuum induction melting
Forming Option
1 Hot rolling process
2 Hot Forging: Electro-hydraulic; High-speed-hydraulic; Oil-hydraulic; Precision-forging
Heat-treatment Option
1 +A: Annealed (full/soft/spheroidizing)
2 +N: Normalized
3 +NT: Normalized and tempered
4 +QT: Quenched and tempered (water/oil)
Suface Option
1 Black Surface
2 Grounded: Bright but rough ; Not precision
3 Machining for plate: Bright and precision; Little turning scar
4 Peeled/Turned: Bright and precision; Little turning scar
5 Polished: Very Bright and precision size; Not turning scar
Other Services
1 Cutting: Small pieces
2 CNC Machine: Produce as your drawing
3 Package: Bare/Nylon/Canvas/Wooden
4 Payment:T/T, L/C, O/A(request credit)
5 Transport:FOB/CFR/CIF/DDU/DDP (train/ship/Air)
5 Workability
Forging: Forging of the W1 tool steel can be performed at 1038°C (1900°F) down to 816°C (1550°F) but not below 843°C (1500°F).
Machinability: The machinability of W1 tool steel is very good as they are plain carbon steels with 100% rating based on which other tool steels are compared.
Forming: W1 tool steel can be easily formed using conventional methods.
Welding: W1 tool steel are weldable using all the standard methods.
Hot Working: W1 tool steel can be hot-worked.
Cold Working: W1 tool steel in the annealed condition have very good ductility and can be easily cold worked using conventional methods.
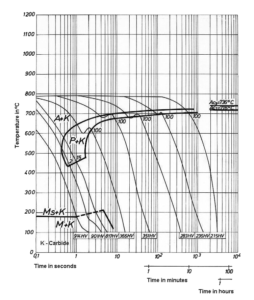
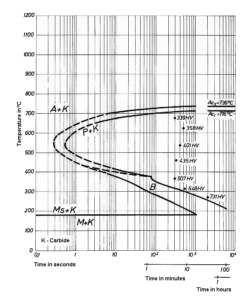
6 HEAT TREATMENT
The treatment depends upon the intricacy of the part or section size. W1 tool steel with large sections or intricate shapes have to be slowly preheated to 593°C (1100°F) and then the temperature should be slowly increased to 816°C (1500°F). The steels should be maintained at the same temperature for 10 to 30 minutes and finally water or brine quenched.
ANNEALING:Annealing has to be performed at 760°C (1400°F) followed by slow furnace cooling at 4°C (40°F) per hour or less.
STRESS RELIEVING: Heat slowly to 1200 to 1250° F. Soak for two hours per
inch of thickness at heat. Soak, slow cool (furnace cool if possible) to room temperature.
HARDENING:
- Preheat: Heat slowly to 1200 to 1250° F. Soak for two hours per inch of thickness at heat. Soak, slow cool (furnace cool if possible) to room temperature.
- Harden: Heat to 1425 to 1475° F. Soak at heat for 30 minutes per inch of thickness.
Temperatures on the high side of the range will increase the depth of the case. - Quench: This material may be water quenched, but brine quenching is preferred. Water or
brine quench to 150 to 200° F. Oil quenching is sometimes used for light sections and where maximum hardness is not required. - Temper: This material may be water quenched, but brine quenching is preferred. Water or
brine quench to 150 to 200° F. Oil quenching is sometimes used for light
sections and where maximum hardness is not required.
w1 steel Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties of W1 steels are tabulated below.
| Properties | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength, ultimate | 1680 MPa | 244000 psi |
| Tensile strength, yield | 1500 MPa | 218000 psi |
| Poisson’s ratio (25°C) | 0.27-0.30 | 0.27-0.30 |
| Elongation at break | 3.50% | 3.50% |
| Bulk modulus | 140 GPa | 20300 ksi |
| Shear modulus | 80.0 GPa | 11600 ksi |
| Elastic modulus | 190-210 GPa | 27557-30458 ksi |
| Charpy impact, unnotched | 86.0 J | 63.4 ft-lb |
| Hardness, Brinell (converted from Rockwell C Hardness) | 498 | 498 |
| Hardness, Knoop (converted from Rockwell C Hardness) | 558 | 558 |
| Hardness, Rockwell C | 50.0-51.0 | 50.0-51.0 |
| Hardness, Vickers (converted from Rockwell C Hardness) | 531 | 531 |
| Machinability (based on AISI 1212 steel as 100% machinability) | 40 | 40 |
Mill′s test certificate
EN 10204/3.1 with all relevant data reg. chem. composition, mech. properties and results of testing.
TOLERANCES
| Diameter | Tolerance | Straightness (max T.I.R. in 12″) |
| To .125 dia. | +/-.0003″ | .005″ |
| .125 thru .499 dia | +/-.0005″ | .005″ |
| .500 thru 2 dia | +/-.0010″ | .005″ |
| USA: AISI W1, UK: BW1, Sweden: USA W1, Germany: 1.1654, Japan: SK2 | ||||
| Chemical composition: C=1.0%, Mn=0.35%, Si=0.3% | ||||
| Property | Value in metric unit | Value in US unit | ||
| Density | 7.83 *10³ | kg/m³ | 488.8 | lb/ft³ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modulus of elasticity | 205 | GPa | 29700 | ksi |
| Thermal expansion (20 ºC) | 10.4*10-6 | ºCˉ¹ | 5.78*10-6 | in/(in* ºF) |
| Specific heat capacity | 461 | J/(kg*K) | 0.11 | BTU/(lb*ºF) |
| Electric resistivity | 3.0*10-7 | Ohm*m | 3.0*10-5 | Ohm*cm |
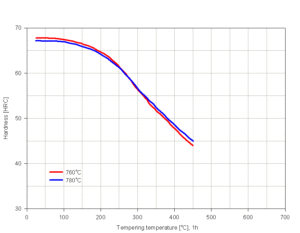
| Annealing temperature | 690…710 | ºC | 1280…1420 | ºF |
| Quenching temperature | 760…780 | ºC | 1400…1440 | ºF |
| Tempering temperature | 100…300 | ºC | 210…570 | ºF |
| Hardness (annealed) | 91 | RB | 91 | RB |
| Hardness (hardened) | 65 | RC | 65 | RC |
| Quenching medium | Water | |||
| Hardening depth | Low | |||
| Resistivity to distortion | Low | |||
| Resistivity to cracking | Low | |||
| Machinability | Very high | |||
| Toughness | High | |||
| Wear resistance | Low | |||
What is W1 steel?
W1 steel is high carbon steel with carbon ranging from 0.6% to 1.4%. With such high carbon, this steel usually has high tensile strength and hardness with low ductility and toughness. That’s why water hardenable tool steel is avoided in applications that require energy absorption or impact loading. Due to excellent machinability characteristics, this high carbon percentage is used extensively for tools used in diverse areas of life.